Learning by (Spaced) Repetition — How Effective is It?
Learning by (Spaced) Repetition — How Effective is It?
In short, very effective
Spaced repetition is an evidence-based learning technique. Though you may not have heard the name, if you’ve ever used apps like Duolingo, Babbel, Memrise, or Anki — you will have used it before.
The basic premise is that items (flashcards, questions, lessons) are reviewed at increasing intervals — until the knowledge is fully embedded into a learner’s long-term memory.
Learning & Memory
Learning is — perhaps unsurprisingly — closely tied with memory.

When you learn something, what you are doing is gaining knowledge and embedding this knowledge into your long-term memory — if you are learning well, that is.
The more effectively you do this, the more effectively you can form a deep understanding of this embedded information — and the more likely it is that you will be able to apply it in useful ways.
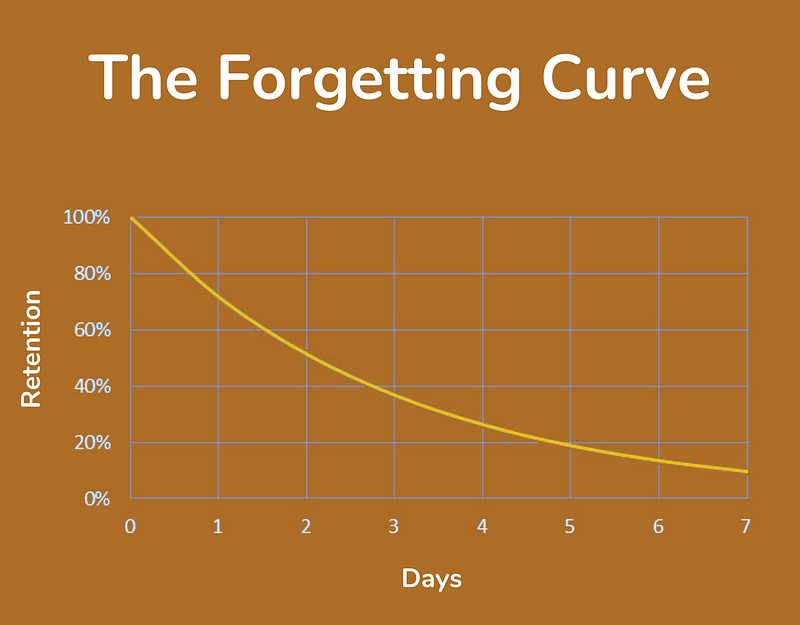
The Forgetting Curve
Hermann Ebbinghaus was a German psychologist known for pioneering the empirical study of memory — he also established the forgetting curve, which models how knowledge is retained (or rather, not retained) over time.
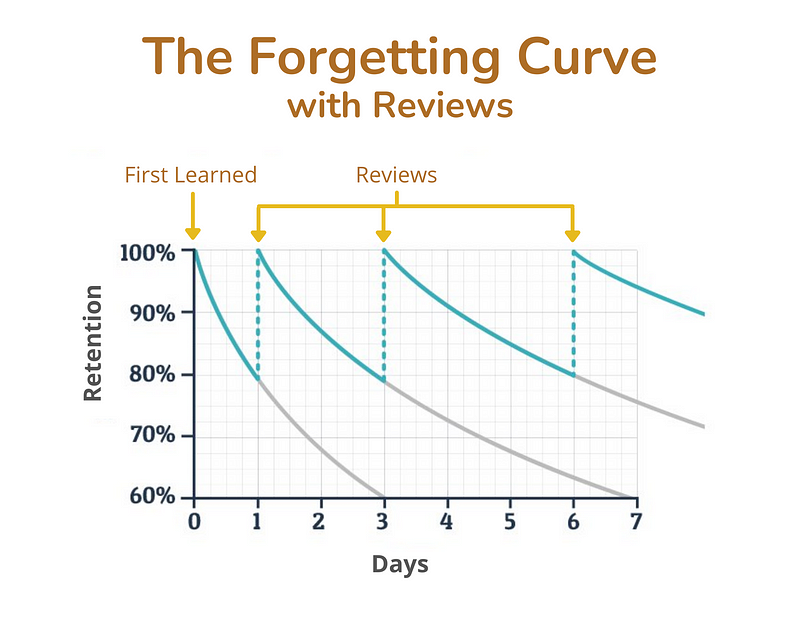
How does Spaced Repetition work?
Spaced repetition aims to solve the problem of forgetting.
Also known as distributed practice, the technique uses some form of an algorithm in order to determine when items should be reviewed by a learner next — and therefore also what are the optimum intervals that should separate the reviews of these individual ‘bits of knowledge’.
Items that are recalled easily will be shown at wider intervals, whilst items that a learner struggles with will be shown in shorter intervals.
How effective is Spaced Repetition?
The examination of the quantitative benefits of spaced repetition started in 1939, with Herbert J. Spitzer —and, since then, an overwhelming body of evidence for the effectiveness of the method has been established.
Now — in 2021 — there are a few things that can be said with relative confidence:
- Spaced repetition is a “highly effective means of promoting learning [over a] variety of settings and across many different types of materials and procedures.” (Dempster, 1989)
- Spaced repetition is effective for people of all ages — usually with little variance in this respect (Toppino, Kasserman, and Mracek, 1991) — for adults, however, spaced repetition is more effective in teaching skills than language (Smith and Scarf, 2017).
- Learning using Spaced Repetition is “cost-effective” and can save organizations money — because more is learned in the same amount of time (Kang, 2016)
- There is some idea of how and why spaced repetition works, biologically speaking — spaced repetition increases the intensity of the neurological activity that is apparent during learning (Feng et al., 2019).
- Quantitatively, the benefit of studying STEM material using spaced repetition (in comparison to massed repetition and ad-hoc study methods) has been found to be statistically significant with a positive effect size of 0.54 (Voice and Stirton, 2020).
How can you use spaced repetition?
As seen above, spaced repetition has stood the test of time as an effective educational tool, supported by over 80 years of research data.
To make use of the technique in your own life, I would recommend using an app like Anki or Memrise — both of which allow you to create flashcards that can be periodically reviewed using spaced repetition. If you are wanting to create a course that makes use of spaced repetition, EdApp allows for that. Beeline is an exciting up-and-coming app that will, amongst other things, provide spaced repetition both for individuals and teachers/trainers — disclaimer, I am involved in this one!
I have used spaced repetition in my learning since finishing my engineering degree in 2016 (how I wish I’d known about it during my studies!) and have used it for language learning (French & isiXhosa) as well as in other domains such as data science. I would highly recommend it when learning any concepts you wish to remember.
Happy learning, and happy remembering!
Graphics have been created by me on Canva unless otherwise stated. Thanks for reading, and hope it was somewhat useful!
References
- Kang, S.H.K. (2016). Spaced Repetition Promotes Efficient and Effective Learning. Policy Insights from the Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 3(1), pp.12–19.
- Smith, C.D. and Scarf, D. (2017). Spacing Repetitions Over Long Timescales: A Review and a Reconsolidation Explanation. Frontiers in Psychology, 8.
- Feng, K., Zhao, X., Liu, J., Cai, Y., Ye, Z., Chen, C. and Xue, G. (2019). Spaced Learning Enhances Episodic Memory by Increasing Neural Pattern Similarity Across Repetitions. The Journal of Neuroscience, 39(27), pp.5351–5360.
- Voice, A. and Stirton, A. (2020). Spaced Repetition: towards more effective learning in STEM. New Directions in the Teaching of Physical Sciences, (15).
- EdApp Microlearning Blog. (2019). Distributed Practice | EdApp Microlearning. [online] Available at: https://www.edapp.com/blog/distributed-practice/.
- Dom Barnard (2018). Overcoming the Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve with Virtual Reality. [online] Virtualspeech.com. Available at: https://virtualspeech.com/blog/overcoming-ebbinghaus-forgetting-curve-virtual-reality.
- The Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica (2019). Hermann Ebbinghaus | German psychologist. In: Encyclopædia Britannica. [online] Available at: https://www.britannica.com/biography/Hermann-Ebbinghaus.
- EdApp Microlearning Blog. (2021). Learning curve | EdApp Microlearning. [online] Available at: https://www.edapp.com/blog/learning-curve/ [Accessed 18 Dec. 2021].
- EdApp Microlearning Blog. (2018). Ebbinghaus forgetting curve | EdApp Microlearning. [online] Available at: https://www.edapp.com/blog/ebbinghaus-forgetting-curve/.
- Ankiweb.net. (2016). Anki — powerful, intelligent flashcards. [online] Available at: https://apps.ankiweb.net/.
- www.edapp.com. (n.d.). Spaced Repetition Tool | EdApp Microlearning. [online] Available at: https://www.edapp.com/spaced-repetition/ [Accessed 18 Dec. 2021].
- EdApp Microlearning Blog. (2019). Spaced Repetition | EdApp Microlearning. [online] Available at: https://www.edapp.com/blog/how-spaced-repetition-works/.
- supermemo.guru. (n.d.). Spaced repetition — supermemo.guru. [online] Available at: https://supermemo.guru/wiki/Spaced_repetition [Accessed 18 Dec. 2021].
- Dempster, F.N. (1989). Spacing effects and their implications for theory and practice. Educational Psychology Review, [online] 1(4), pp.309–330. Available at: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF01320097.
- Toppino, T.C., Kasserman, J.E. and Mracek, W.A. (1991). The effect of spacing repetitions on the recognition memory of young children and adults. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 51(1), pp.123–138.
- Scribbr. (2020). What is Effect Size and Why Does It Matter? [online] Available at: https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/effect-size/.
- EdApp Microlearning Blog. (2020). What is the evidence around spaced repetition | EdApp Microlearning. [online] Available at: https://www.edapp.com/blog/evidence-around-spaced-repetition/ [Accessed 18 Dec. 2021].